Introduction
Existing Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) are static and created by ERC721 standard in Ethereum to represent ownership of unique assets, which have two limitations:
- NFT tokens are static and isolated from the off-chain environment;
- ERC721 tokens are limited to Ethereum that cannot be accessible from other blockchains.
RareLink Protocol is a new initiative to create “dynamic” NFTs and provide a two-way token bridge between Ethereum and Polkadot:
- First minting platform to create “dynamic” NFT in both Ethereum and Polkadot. “dynamic” NFT can interact with off-chain environment through Oracle services like Chainlink;
- A new token bridge is created to enables two-way transfer of both “static” and “dynamic” NFTs between Ethereum and Polkadot to access more liquidity in more marketplaces and DeFi applications;
Concept
Background
There are various bridges existing in the market, aiming to establish cross-chain connections among different chains.
POA TokenBridge
The POA TokenBridge provides a generic bridge between Ethereum based chains. Multiple bridge modes are supported by POA TokenBridge, for different purposes of data transfer, e.g. ERC20 to ERC20, AMB(Arbitrary Message Bridge). With the AMB mode, arbitrary messages can be transferred across chains, which means NFTs can be also transferred between networks via this bridge mode.
Proof of Concept
With the implementation of POA TokenBridge, a cross-chain bridge between Ethereum and Polkadot can be easily established. With the benefit of Substrate, we are able to establish a parachain of Polkadot with EVM Pallet. And the POA bridge will perfectly fit the gap between the EVM Pallet equipped parachain of Polkadot and the Ethereum network, and connect these two networks to communicate from each other.
However, this solution requires offline oracle nodes to relay and forward messages from both direction, and it is still heavily relying on the EVM environment and Solidity contracts on Polkadot side. It is not a native solution for Polkadot.
In order to make full use of the existing resources, and to maximize the power of Substrate, we plan to implement the whole oracle part with Off-Chain Workers inside our Runtime. The benefits of doing this are:
- Security improvement of on-chain implementation comparing to offline oracles
- Better performance with native code implementation
- Easy to access chain states
Moreover, with the flexibility of Runtime implementation, we will add support of dynamic NFT from ChainLink in the future development phase.
Architecture
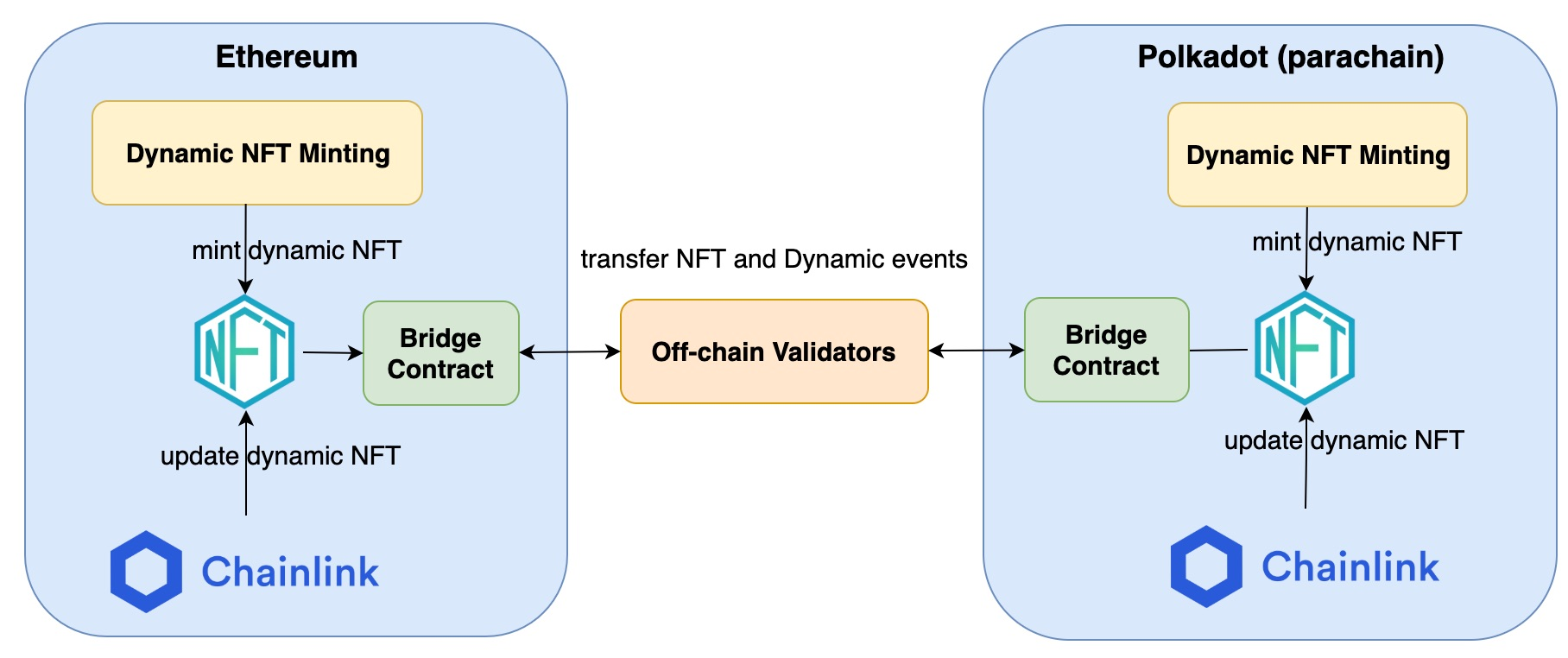
RareLink Protocol has following key modules, which are “first-of-kind” in both Ethereum and Polkadot:
- Dynamic NFT Minting: users can create their own dynamic NFT in this minting platform for their unique assets. The NFT is dynamic and responsive to the off-chain events. For example, it can be burnt after a specific expiration date or upgrade itself upon a specific off-chain event reported from ChainLink.
- Token Bridge for dynamic NFTs:
- RareLink provides a “first-of-kind” two-way bridge which can transfer both “static” and “dynamic” NFT along with corresponding events (e.g., upgrade NFTs) across Blockchains.
- The oracle service triggers the token contract to upgrade dynamic NFT in the original network, while the token has been transferred to another blockchain. It is required for token bridge to transfer the “dynamic” events across blockchain networks to update transferred NFTs.
- Existing bridge projects can only transfer tokens. Therefore, they are not fit for “dynamic” NFTs.
FAQ
Why dynamic NFT is important?
- Most existing NFTs are static and created by ERC721 standard, so they are limited to Ethereum network and won’t response to real-world events;
- There are a lot of business use cases demand dynamic NFT (e.g., ticketing, sports, etc.), where NFTs need to dynamically response to real-world events (such as time, market price, weather data, flight status, etc.) and update themselves in real-time.
- With the help of dynamic NFT, tons of new applications will be enabled and it will become the next revolution in NFTs and Blockchain domain.
- See more use cases currently from Chainlink blog.
Why a new token bridge is needed for dynamic NFT? What is the difference from existing token bridge?
- All existing token bridges (e.g., POA token bridge, Parity token bridge, and ChainSafe/Centrifuge chainbridge) are implemented to transfer static tokens such as ERC20 or ERC721 tokens.
- They are not able to relay the update events for dynamic NFTs, therefore, the dynamic NFTs will lose dynamic behavior after cross-chain transfer. Literally, they become static NFTs afterwards. Therefore, existing bridges are not suitable.
- The unique characteristic of dynamic NFTs require a new token bridge to keep track of their dynamic behavior across different networks.
- RareLink protocol aims to close the gap and create a new two-way bridge for dynamic NFT to enable more business use cases in both ecosystems.
What is the challenge to build a new token bridge for dynamic NFT?
-
The first challenge is the relay of update events:
- The update event is triggered in one blockchain and needs to be passed to another blockchain, which can be an arbitrary message used to retain the same dynamic behavior across networks.
- It is a great challenge to transfer the update even across the bridge with high fidelity and update the dynamic NFT correctly.
-
The second challenge is to provide high reliability:
- The token transfer may fail due to various reasons (e.g., message queue is broken, event message is failed to be received, etc.) and user will lose their tokens in that case.
- RareLink protocol will keep high reliability as the top priority in the design of the new token bridge. Many new techniques (e.g., retrying, validation, etc.) will be created for this purpose.